https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17070
17070번: 파이프 옮기기 1
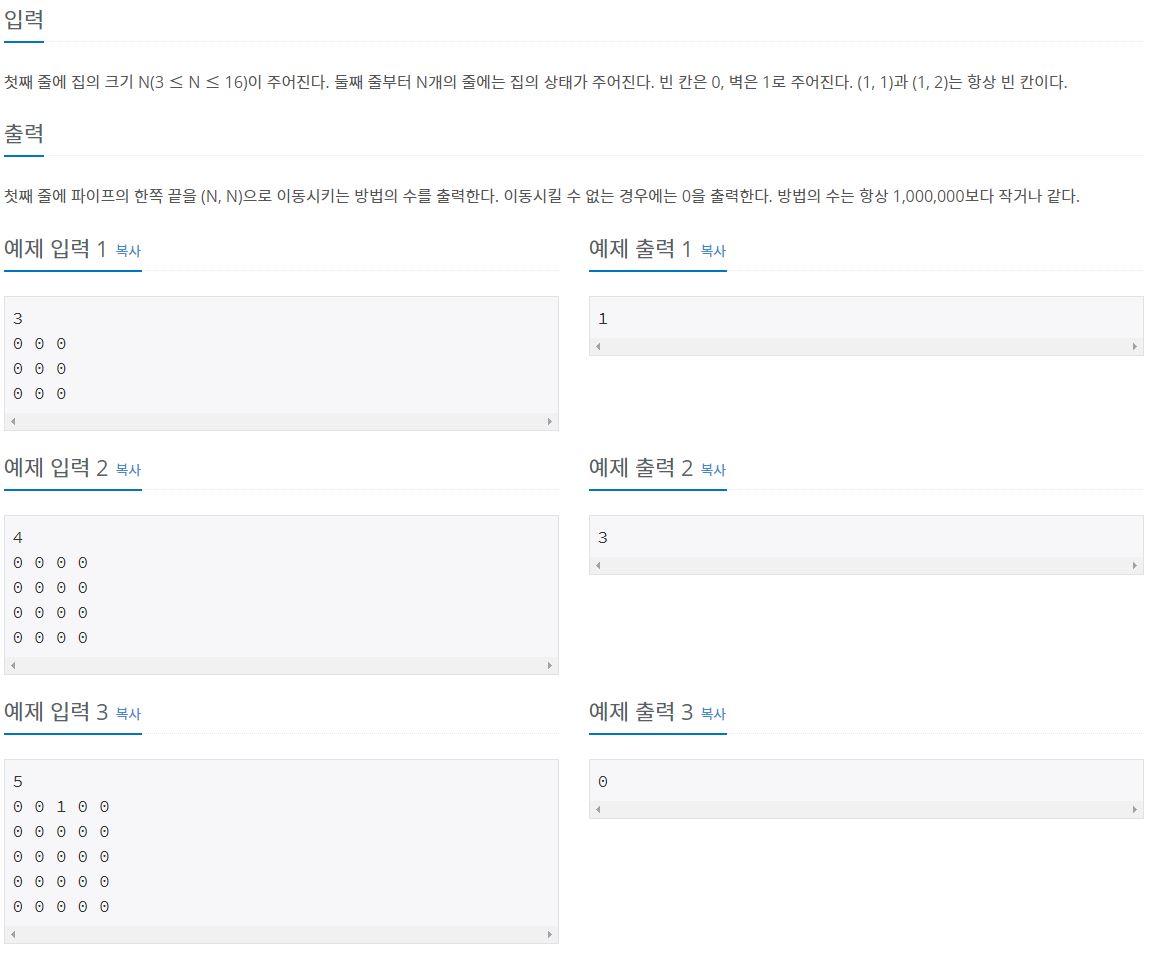
유현이가 새 집으로 이사했다. 새 집의 크기는 N×N의 격자판으로 나타낼 수 있고, 1×1크기의 정사각형 칸으로 나누어져 있다. 각각의 칸은 (r, c)로 나타낼 수 있다. 여기서 r은 행의 번호, c는 열의
www.acmicpc.net



오늘도 알고리즘 오늘도 코테준비!
특정 상황에 맞게 특정 조건을 구현해 줘야 하는 문제입니다.
오른쪽 밑으로 내려오는 파이프는 괜찮지만 대각선으로 내려가는 파이프는 4칸을 필요로 한다는점!
그리고 파이프가 90도로 안꺽이기때문에 각 파이프 타입별로 기억하기 위해서
재귀를 돌때 파이프의 현재 상태를 들고 다녀야 한다는 점만 기억하시면 쉽게 접근하실 수 잇는 난이도라고 생각합니다.
방문처리를 하지 않아도 되는 내려가기만 하는 파이프이기 때문에 한번 재미있게 짜보실 수 있다고 생각합니다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int N, res;
static int map[][];
static int dr[] = { 0, 1, 1 };
static int dc[] = { 1, 1, 0 };
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
map = new int[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
map[0][0] = 1;
map[0][1] = 1;
dfs(0, 1, 0);
System.out.println(res);
}
static void dfs(int r, int c, int type) {
if (r == N - 1 && c == N - 1) {
res++;
//print(map);
return;
}
if (type == 0 && c == N - 1) { // 오른쪽이나 밑 끝에 닿은경우 리턴
return;
}
if (type == 2 && r == N - 1) { // 오른쪽이나 밑 끝에 닿은경우 리턴
return;
}
if(type == 0) {
for (int d = 0; d < 2; d++) {
int nr = r + dr[d];
int nc = c + dc[d];
if (nr >= N || nc >= N)
continue;
if (map[nr][nc] == 0 ) {
if (d == 1 && (map[nr - 1][nc] == 1 || map[nr][nc - 1] == 1)) {
continue;
}
map[nr][nc] = 1;
dfs(nr, nc, d);
map[nr][nc] = 0;
}
}
}
if (type == 1) {
for (int d = 0; d < 3; d++) {
int nr = r + dr[d];
int nc = c + dc[d];
if (nr >= N || nc >= N)
continue;
if (map[nr][nc] == 0) {
if (d == 1 && (map[nr - 1][nc] == 1 || map[nr][nc - 1] == 1)) {
continue;
}
map[nr][nc] = 1;
dfs(nr, nc, d);
map[nr][nc] = 0;
}
}
}
if(type == 2) {
for (int d = 1; d < 3; d++) {
int nr = r + dr[d];
int nc = c + dc[d];
if (nr >= N || nc >= N)
continue;
if (map[nr][nc] == 0) {
if (d == 1 && (map[nr - 1][nc] == 1 || map[nr][nc - 1] == 1)) {
continue;
}
map[nr][nc] = 1;
dfs(nr, nc, d);
map[nr][nc] = 0;
}
}
}
}
static void print(int map[][]) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
}
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2636 : 치즈 (Java) (0) | 2020.10.10 |
|---|---|
| 백준 17070 : 파이프 옮기기 1 (DP) (Java) (0) | 2020.10.02 |
| 백준 1197 : 최소 스패닝 트리 (Java) (0) | 2020.09.05 |
| 백준 16236 : 아기 상어 (Java) (0) | 2020.09.04 |
| 백준 17472 : 다리 만들기 2 (Java) (0) | 2020.09.04 |